Over 2 million + professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Unlock the essentials of corporate finance with our free resources and get an exclusive sneak peek at the first module of each course. Start Free
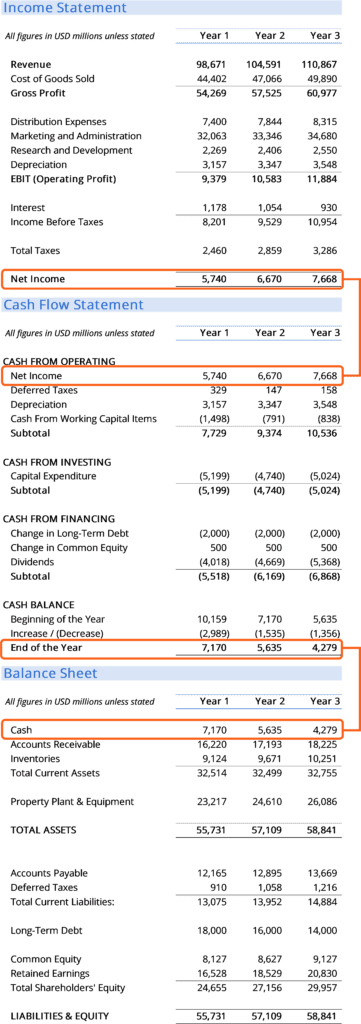
The three financial statements are (1) the income statement, (2) the balance sheet, and (3) the cash flow statement. Each of the financial statements provides important financial information for both internal and external stakeholders of a company.
The income statement illustrates the profitability of a company under accrual accounting rules. The balance sheet shows a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a particular point in time. The cash flow statement shows cash movements from operating, investing, and financing activities.
These three core statements are intricately linked to each other and this guide will explain how they all fit together. By following the steps below, you’ll be able to connect the three statements on your own.

Often, the first place an investor or analyst will look is the income statement. The income statement shows the performance of the business throughout each period, displaying sales revenue at the very top. The statement then deducts the cost of goods sold (COGS) to find gross profit.
From there, gross profit is impacted by other operating expenses and income, depending on the nature of the business, to reach net income at the bottom — “the bottom line” for the business.
The balance sheet displays the company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a point in time. The two sides of the balance sheet must balance: assets must equal liabilities plus equity. The asset section begins with cash and equivalents, which should equal the balance found at the end of the cash flow statement.
The balance sheet then displays the ending balance in each major account from period to period. Net income from the income statement flows into the balance sheet as a change in retained earnings (adjusted for payment of dividends).
The cash flow statement then takes net income and adjusts it for any non-cash expenses. Then cash inflows and outflows are calculated using changes in the balance sheet. The cash flow statement displays the change in cash per period, as well as the beginning and ending balance of cash.
| Income Statement | Balance Sheet | Cash Flow | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Period of time | A point in time | Period of time |
| Purpose | Profitability | Financial position | Cash movements |
| Measures | Revenue, expenses, profitability | Assets, liabilities, shareholders' equity | Increases and decreases in cash |
| Starting Point | Revenue | Cash balance | Net income |
| Ending Point | Net income | Retained earnings | Cash balance |
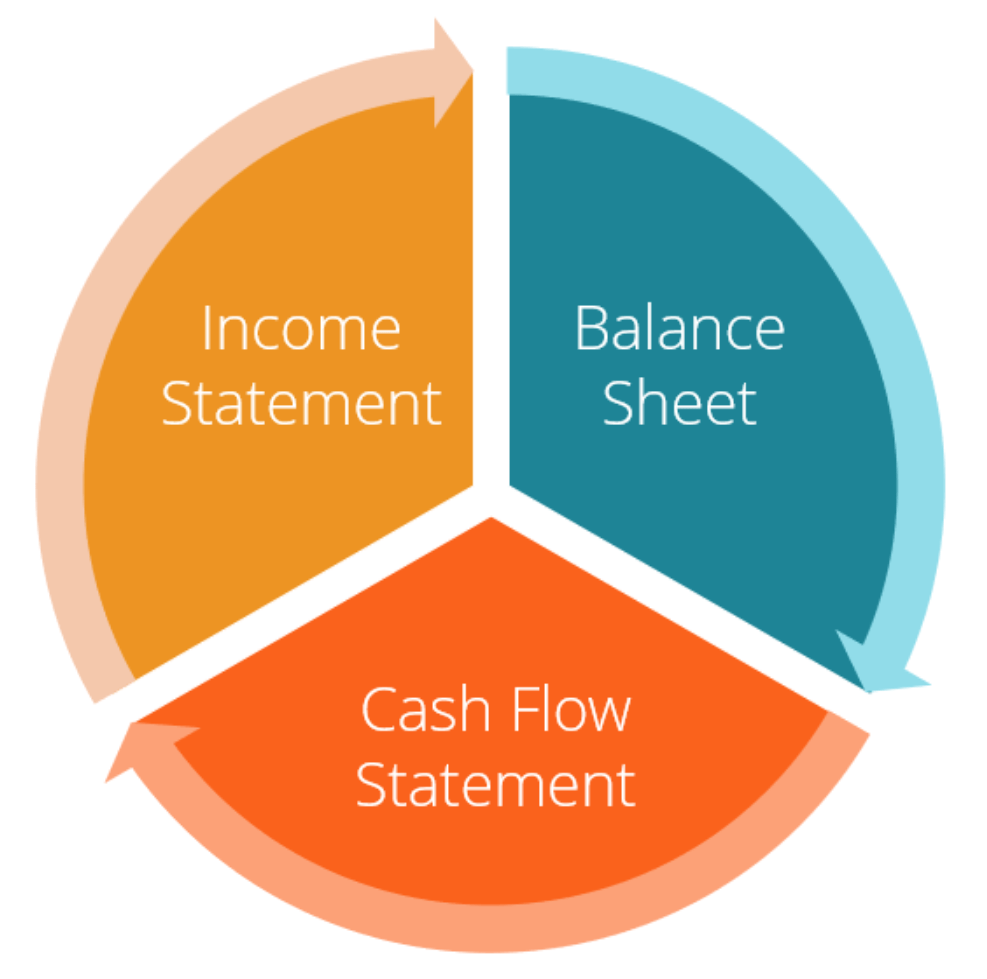
Each of the three financial statements has an interplay of information. Financial models use the trends in the relationship of information within these statements, as well as the trend between periods in historical data to forecast future performance.
The preparation and presentation of this information can become quite complicated. In general, however, the following steps are followed to create a financial model.
CFI is a global provider of financial modeling courses and of the FMVA Certification. CFI’s mission is to help all professionals improve their technical skills. If you are a student or looking for a career change, the CFI website has many free resources to help you jumpstart your Career in Finance. If you are seeking to improve your technical skills, check out some of our most popular courses. Below are some additional resources for you to further explore:
CFI is a global provider of financial modeling courses and of the FMVA Certification. CFI’s mission is to help all professionals improve their technical skills. If you are a student or looking for a career change, the CFI website has many free resources to help you jumpstart your Career in Finance. If you are seeking to improve your technical skills, check out some of our most popular courses. Below are some additional resources for you to further explore:
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
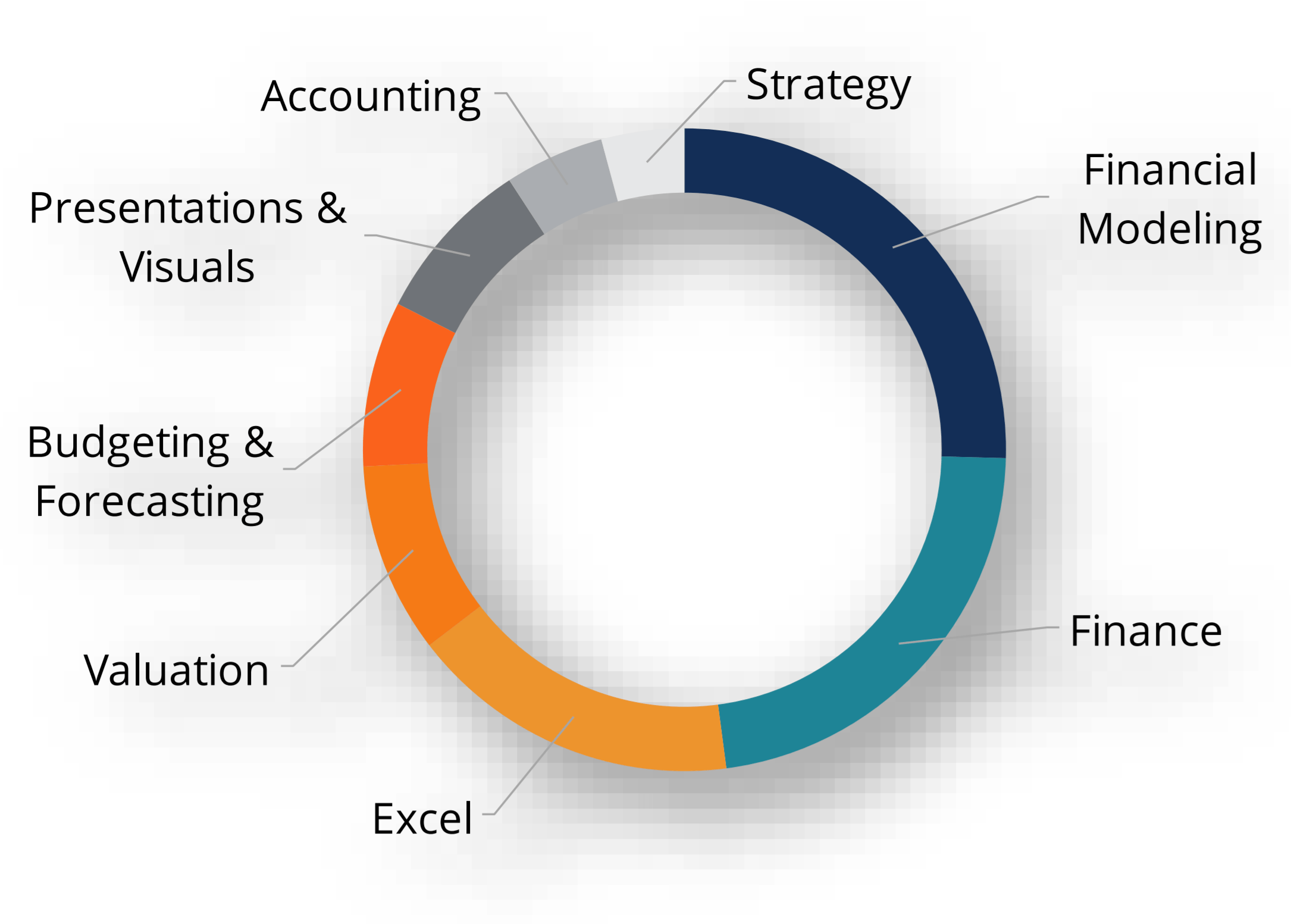
A well rounded financial analyst possesses all of the above skills!
CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path.
In order to become a great financial analyst, here are some more questions and answers for you to discover:
CFI is a global provider of financial modeling courses and of the FMVA Certification. CFI’s mission is to help all professionals improve their technical skills. If you are a student or looking for a career change, the CFI website has many free resources to help you jumpstart your Career in Finance. If you are seeking to improve your technical skills, check out some of our most popular courses. Below are some additional resources for you to further explore:
to take your career to the next level and move up the ladder!
Get Certified for Financial Modeling (FMVA)®Gain in-demand industry knowledge and hands-on practice that will help you stand out from the competition and become a world-class financial analyst.